Unlocking the Future: A Deep Dive into Industrial 3D Printing Technology
In a rapidly transforming industrial landscape, there’s a cutting-edge technology poised to revolutionize the way we manufacture products and design solutions: Industrial 3D Printing. A blend of engineering innovation and creative mastery, it’s not merely a new production method but a profound shift in the world of manufacturing.

What is Industrial 3D Printing Technology?
Industrial 3D Printing, often termed as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer, directed by digital 3D models. In essence, it turns digital designs into tangible products. It has become a critical asset in modern industry, enabling unprecedented levels of customization, flexibility, and speed.
How Does Industrial 3D Printing Differ from Traditional Manufacturing?
Unlike conventional techniques, which often involve subtracting material to create an object, 3D printing adds it, creating a paradigm shift in production.
Traditional Manufacturing:
Subtractive processes
Mold-based
Mass production-centric
Limited customization
High wastage
Industrial 3D Printing:
Additive processes
Digital blueprint-centric
Tailored production
Enhanced customization
Minimal waste
What are the Types of Industrial 3D Printing Technologies?
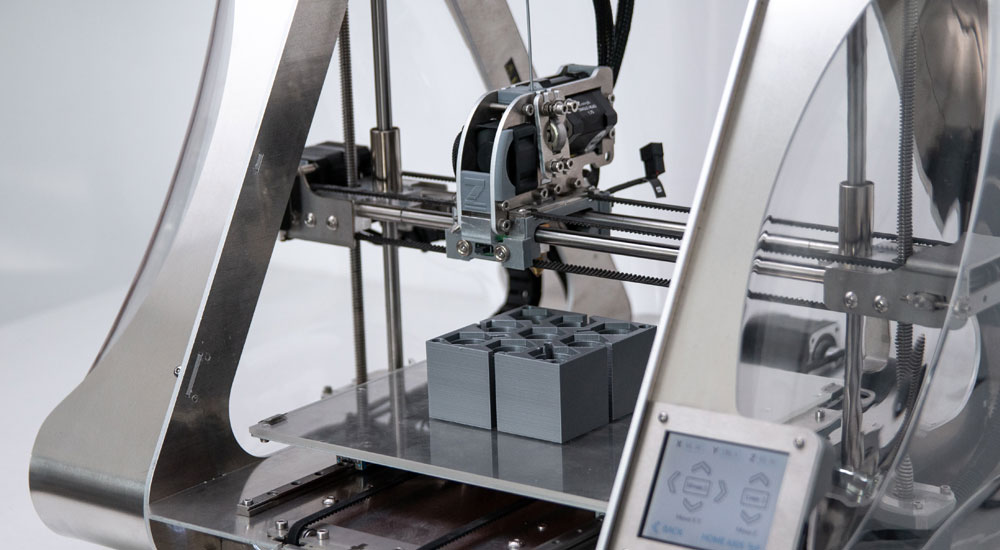

Delving deeper into the world of 3D printing, several technologies emerge, each with its unique method and specific applications.
What is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)?
FDM works by extruding thermoplastic filaments, layer by layer, to craft an object. It’s renowned for its affordability and is ideal for prototyping.
What is Stereolithography (SLA)?
SLA employs a laser to solidify liquid resin in precise patterns, creating highly detailed models. It stands out for its exceptional resolution.
What is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
In SLS, a laser sinters powdered material, fusing them to form a solid structure. It is versatile and can be used with metals, ceramics, and some plastics.
What is Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)?
DMLS is an evolution of SLS, designed specifically for metal powders. This technique produces robust and intricate metal parts.
What is Electron Beam Melting (EBM)?
EBM uses an electron beam to melt metal powder, layer by layer, in a vacuum. This method produces dense and strong components, particularly suited for aerospace applications.
What Materials Can Be Used in Industrial 3D Printing?
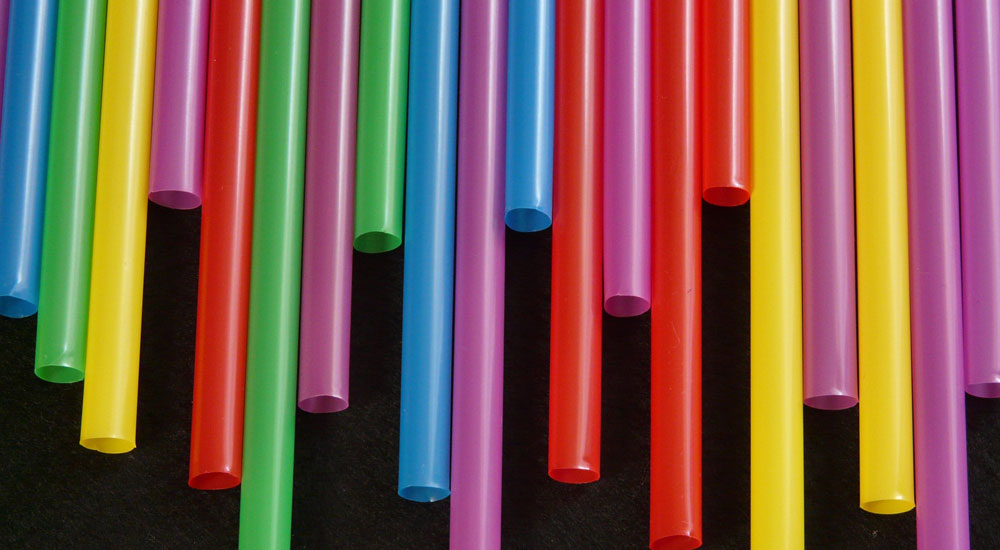

A diverse range of materials can be leveraged in 3D printing, each offering unique attributes.
Plastics and Polymers:
Frequently used due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Examples include PLA, ABS, and TPU.
Metals:
Suited for applications demanding strength. Common metals include titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Ceramics:
Known for their hardness and thermal resistance, ceramics like zirconia and alumina are now printable.
Composite Materials:
Composites combine properties of multiple materials. Carbon fiber-reinforced composites are a popular choice.
How Does Industrial 3D Printing Impact the Supply Chain?
The influence of 3D printing on supply chains is profound:
Diminished inventory needs, thanks to on-demand production.
Accelerated manufacturing speed, shortening lead times.
Enhanced customization possibilities.
Significant reduction in waste.
What are the Applications of Industrial 3D Printing Across Industries?
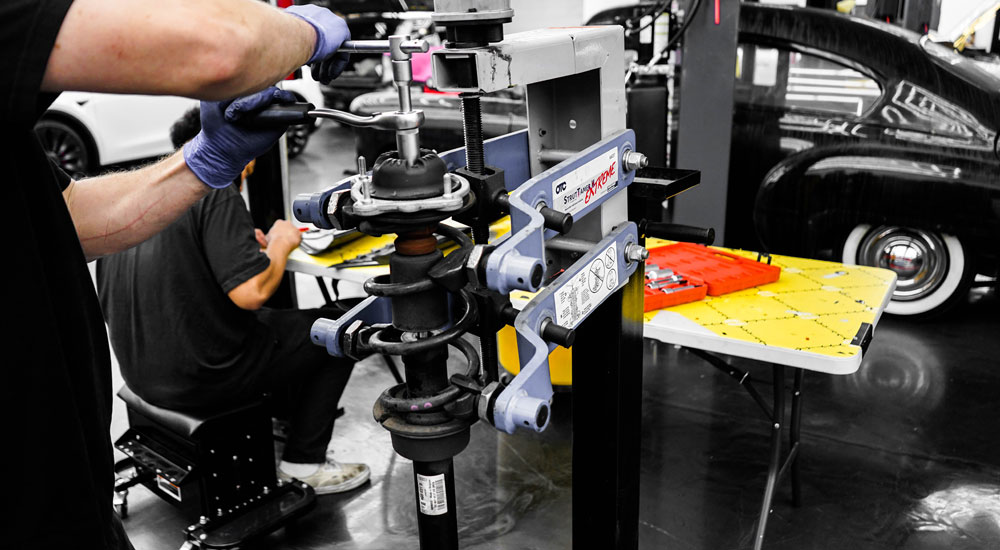

Various sectors are reaping the rewards of 3D printing.
Aerospace and Defense:
Components, prototypes, and even drones are being 3D printed.
Automotive:
From car parts to entire chassis, the auto industry is undergoing a transformation.
Healthcare and Dental:
Custom implants, prosthetics, and dental solutions are made possible with 3D printing.
Consumer Goods:
From toys to bespoke jewelry, the possibilities are limitless.
Construction:
3D printed homes and architectural models are becoming a reality.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Industrial 3D Printing?
Like any technology, 3D printing offers both advantages and challenges.
Benefits:
Personalized products
Swift prototyping
Cost savings for limited runs
Waste minimization
Simplified supply chains
Limitations:
Restricted materials range
Necessity of post-production
Slower for bulk manufacturing
Initial cost barriers
How to Choose the Right 3D Printing Process for Your Needs?
Several factors influence this decision, such as cost implications, material choices, desired resolution, and last but not least, the right 3D printer. For your specific needs, you can choose 3D printers by Raise3D.
What Are the Cost Implications?
Costs vary based on technology. FDM is generally more affordable, while DMLS or EBM can be pricier due to material and process intricacies.
How to Evaluate Material Choices for Your Application?
Consider the desired strength, flexibility, and finish.
How to Determine the Best Print Resolution and Layer Height?
This depends on the intended application. Prototypes might not need high resolution, but final products usually do.
Safety and Environmental Considerations in Industrial 3D Printing

Like any industrial process, 3D printing presents both safety and environmental challenges.
What are the Safety Protocols?
Work in well-ventilated areas, use protective equipment, and adhere to manufacturer guidelines.
How Does 3D Printing Impact the Environment?
On one hand, it reduces waste, but energy consumption and plastic use are concerns.
Future of Industrial 3D Printing: Where is it Heading?
Advancements are constant, with new materials and methods on the horizon.
What are the Emerging Materials and Technologies?
Biodegradable plastics and even organic tissues are becoming printable.
How Might 3D Printing Reshape Global Manufacturing Dynamics?
Localized manufacturing could reduce global shipping and associated emissions.
How Can Businesses Adopt and Integrate 3D Printing Into Their Operations?
To integrate 3D printing, businesses should:
Understand their specific needs
Evaluate different technologies
Train staff adequately
Establish a prototyping phase
Scale up strategically
Conclusion
Industrial 3D printing, a game-changer in the realm of manufacturing, is reshaping industries, enhancing capabilities, and presenting novel challenges. As it continues to mature, the only certainty is its profound and lasting impact on the world of production.
Recent Comments